Microstrip lines¶
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated with any technology where a conductor is separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as “substrate”. Microstrip lines are used to convey microwave-frequency signals.
By design, the microstrip line is a dielectric substrate on which a metal strip is applied.
When a wave propagates along a microstrip line, part of the field goes out, since the microstrip line does not have metal borders on all sides, unlike, for example, rectangular waveguides.
Effective permittivity of microstrip line
Imagine an environment in which the field will have the same magnitude as the field of a microstrip line. The (relative) permittivity of such a medium will be called the effective (relative) permittivity of the line. See image below.
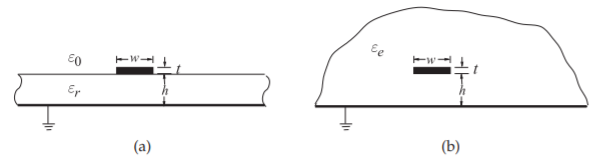
Effective width of microstrip line
Effective width of a microstrip line is the width of such a flat capacitor, the electric intensity between the plates of which is equal to the electric intensity in the dielectric of the substrate under the line strip.
Contents:
- Attenuation coefficient in dielectric substate of microstrip line
- Attenuation coefficient in metal of microstrip line when width is greater than thickness
- Attenuation coefficient in microstrip metal when thickness is greater than width times \(2 \pi\)
- Attenuation coefficient in microstrip metal when thickness is less than width times \(2 \pi\)
- Effective permittivity of microstrip line when width is greater than thickness
- Effective permittivity of microstrip line when width is less than thickness
- Effective permittivity of microstrip line from frequency
- Effective width of microstrip line when width is greater than thickness
- Effective width of microstrip line when width is less than thickness
- Inductance of microstrip line strip
- Resistance of microstrip line
- Short circuit inductance of microstrip line
- Surge impedance of microstrip line from frequency